| Lesson 7 | Link multiple sites |
| Objective | Create site links |
Using Site links to establish cost-effective Replication Model
By associating sites with site links, you define values for your network model that provide the most cost-effective replication.
Active Directory creates a default site link named DEFAULTIPSITELINK. If you do not create new site links manually or modify the settings for the default site link, replication occurs using the default site link values. As you can see, the KCC uses specified values for cost, interval, and schedule. Let's review each of these.
Active Directory creates a default site link named DEFAULTIPSITELINK. If you do not create new site links manually or modify the settings for the default site link, replication occurs using the default site link values. As you can see, the KCC uses specified values for cost, interval, and schedule. Let's review each of these.
Assigning Cost range Replication Value
The site link cost[1] is an arbitrary number rather than an actual cost. You assign cost values to site links to reflect the bandwidth associated with each connection; higher cost values reflect slower connections. You can set a site link cost from 1 to 32767. By default, the cost of a site link is 100. The cost is set in the properties sheet for the <site name> object, which is located in the console tree under IP or SMTP (depending on the protocol used for the site link).
Because technologies and hardware are constantly improving, you should assign site link costs with the following in mind:

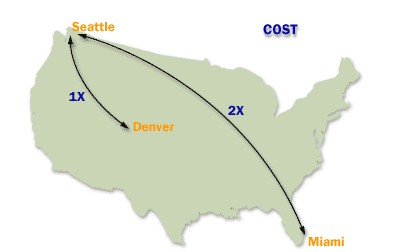
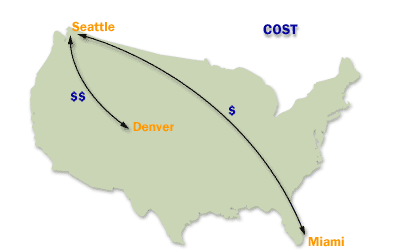
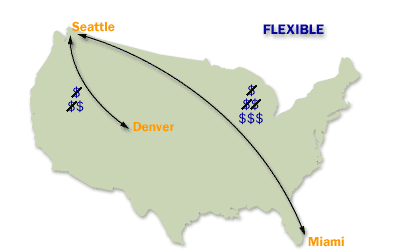
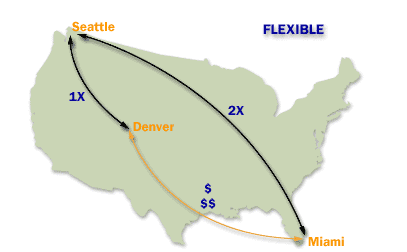
Factors to consider when assigning "Site Link Costs" in Active Directory
When assigning "Site Link Costs" in Active Directory (AD), it is essential to consider various factors to ensure efficient and reliable replication across the network. Site link costs are used by AD to determine the most cost-effective replication path between AD sites. These costs are numerical values assigned to site links, reflecting the relative expense or speed of communication over those links. Here are the key factors to consider:
In summary, assigning site link costs in Active Directory requires a comprehensive evaluation of network characteristics, business requirements, and the operational environment. Balancing these factors effectively will help ensure that AD replication is both efficient and resilient.
- Network Bandwidth: The available bandwidth between sites is a critical factor. Higher bandwidth connections can handle more data and should generally have a lower cost to reflect their desirability for replication traffic.
- Network Latency: The time it takes for data to travel between sites can significantly affect replication efficiency. Links with lower latency should be assigned lower costs, as they allow for quicker replication.
- Link Reliability: Consider the stability and reliability of each network link. More reliable connections should be assigned lower costs, as they are less likely to disrupt replication processes.
- Replication Traffic: Assess the volume of replication traffic expected between sites. Sites with higher traffic volumes may require links with lower costs to prioritize their replication needs.
- Cost of Communication: If there are financial costs associated with using certain network links (e.g., leased lines or VPNs with usage charges), this should be factored into the site link cost. More expensive links should generally have higher costs to minimize unnecessary use.
- Physical Topology: The physical layout of your network and the geographical distance between sites can influence site link costs. Longer distances often mean higher latency and potentially lower reliability, which should be reflected in the costs.
- Redundancy and Failover: Design your AD topology with redundancy in mind. Assign costs in a way that supports alternative replication paths in case of link failures, without causing excessive replication traffic over less desirable links.
- Administrative Overhead: Consider the management and monitoring overhead associated with different links. Links that require more administrative effort to maintain may warrant higher costs to discourage their use unless necessary.
- Security Constraints: Security requirements can also influence site link costs. Links that pass through less secure environments might be assigned higher costs to reduce their use for sensitive replication traffic.
- Change Management: Implement a process for regularly reviewing and adjusting site link costs as network conditions, business requirements, or AD topology changes. This ensures that the AD replication remains optimized over time.
In summary, assigning site link costs in Active Directory requires a comprehensive evaluation of network characteristics, business requirements, and the operational environment. Balancing these factors effectively will help ensure that AD replication is both efficient and resilient.
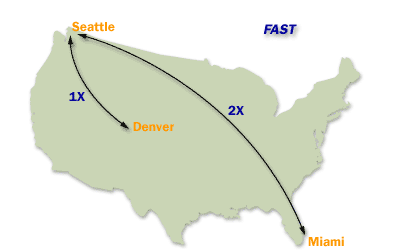
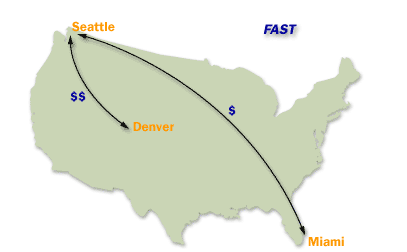
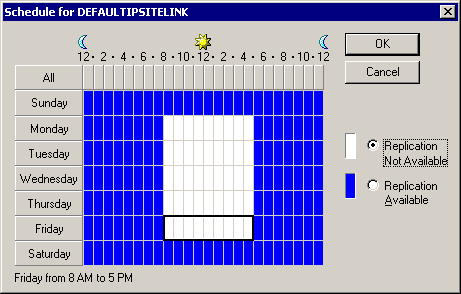
- Assigning an interval Replication Value: The interval setting defines the frequency of replication.
The replication interval must be at least 15 minutes and no more than 10080 minutes (or one week) in length. By default, replication occurs every three hours (an interval setting of 180). - Assigning a Schedule Replication ValueAssigning a Schedule Replication Value: The schedule designates when the site link is available. By default, replication can occur any time. Over a slow link, you may choose to adjust the schedule so that replication occurs only during off-peak hours. The schedule and the interval are used together. Replication occurs only at the times allowed by the schedule, and during those times, it occurs as often as the interval allows.
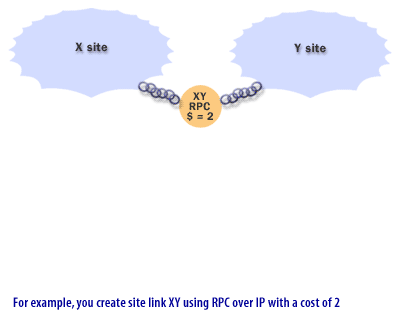
Site Link Bridges
A site link bridge is an object that represents a set of site links,
all of whose sites communicate with the same protocol. The Slide show below describes how the cost of a site link bridge is measured:
Cost of Site Link Bridges
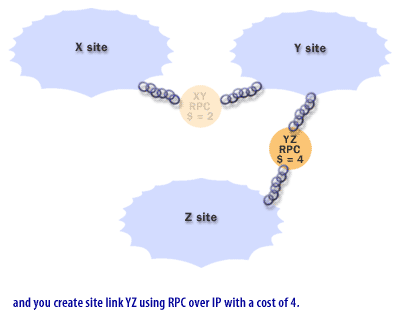
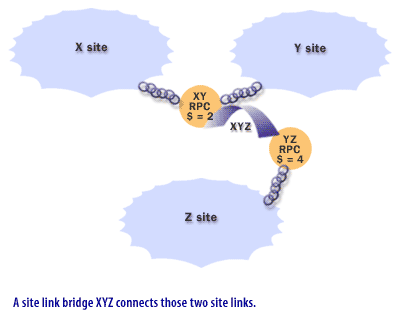
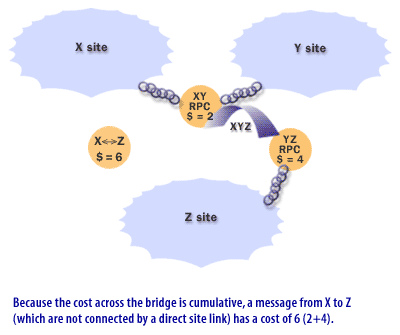
What are Site Link Bridges in Active Directory
In Active Directory, a site link bridge is a logical connection between two or more site links that enables domain controllers in different sites to replicate directory data with each other, even if the sites are not directly connected by a site link. Site link bridges are used to replicate directory data between sites in a multiple-site network when there are multiple hops or intermediaries between the sites.
For example, consider a network with three sites (Site A, Site B, and Site C) and two site links (Site A-Site B and Site B-Site C). Without a site link bridge, domain controllers in Site A and Site C would not be able to replicate directory data with each other directly. However, if you create a site link bridge between the two site links, the domain controllers in Site A and Site C will be able to replicate directory data with each other through Site B.
For example, consider a network with three sites (Site A, Site B, and Site C) and two site links (Site A-Site B and Site B-Site C). Without a site link bridge, domain controllers in Site A and Site C would not be able to replicate directory data with each other directly. However, if you create a site link bridge between the two site links, the domain controllers in Site A and Site C will be able to replicate directory data with each other through Site B.
To configure a site link bridge in Active Directory, follow these steps:
In summary, a site link bridge in Active Directory is a logical connection between two or more site links that enables domain controllers in different sites to replicate directory data with each other, even if the sites are not directly connected by a site link. Configuring a site link bridge involves creating the bridge and modifying the properties of the bridge to control the frequency, schedule, cost, and transport protocol for replication between the sites.
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console. You can do this by going to Start > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Sites and Services.
- In the console tree, expand the Sites container and then select the Inter-Site Transports folder.
- Right-click the folder and select New Site Link Bridge.
- In the New Object, Site Link Bridge dialog box, enter a name for the site link bridge and select the site links that you want to include in the bridge.
- Click OK to create the site link bridge.
- To modify the properties of the site link bridge, right-click the site link bridge and select Properties.
- In the Properties dialog box, you can modify the following settings:
- Replication Frequency: This setting determines how often replication between the sites will occur.
- Replication Schedule: This setting determines the specific times when replication between the sites will occur.
- Cost: This setting determines the relative cost of using the site link bridge for replication. Higher cost values are used for slower or more expensive links.
- Transport: This setting determines the transport protocol that will be used for replication over the site link bridge. The default transport is the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) over IP.
- Click OK to save your changes.
In summary, a site link bridge in Active Directory is a logical connection between two or more site links that enables domain controllers in different sites to replicate directory data with each other, even if the sites are not directly connected by a site link. Configuring a site link bridge involves creating the bridge and modifying the properties of the bridge to control the frequency, schedule, cost, and transport protocol for replication between the sites.
The practical implications of an expensive site link
What are the ramifications of an expensive site link, and do administrators need to know what this cost is? A high-cost link uses more network bandwidth. The ramifications of this may include the following:
- Data transfers between the sites slow down.
- Users logging on across a link may be unable to use network resources until they are logged on.
- Overall performance of the network decreases.
Site links are transitive
By default, all site links are considered transitive.
This means that if there is a link from A to B and a link from B to C, then A is linked implicitly to C. Site links are transitive because all site links for a given protocol implicitly belong to a single site link bridge.
Site link bridge configuration
In a fully routed IP network, no site link bridge configuration is needed. If your IP network is not fully routed, you can turn off the transitive site link feature for the IP transport, in which case you must configure site link bridges manually. In the next lesson, you will learn about monitoring replication traffic.
[1] Site link cost: A way of comparing the efficiency and desirability of using a particular site link based on speed, impact on the network and other factors.