| Lesson 2 | Disaster protection feature in Windows 2000 |
| Objective | Define the basic types of disaster protection. |
Windows Disaster Protection
Windows 2000 provides a variety of both new and enhanced disaster protection features, including support for fault-tolerant volumes, advanced startup options, the Recovery Console, and the Backup utility. Understanding these features is essential to developing and implementing effective disaster protection and recovery plans.
The following Slide Show describes the disaster protection features in Windows 2000:
The following Slide Show describes the disaster protection features in Windows 2000:
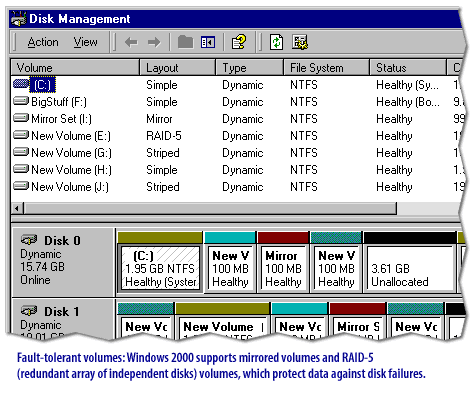
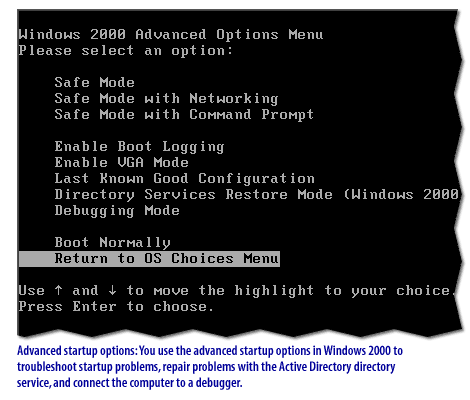
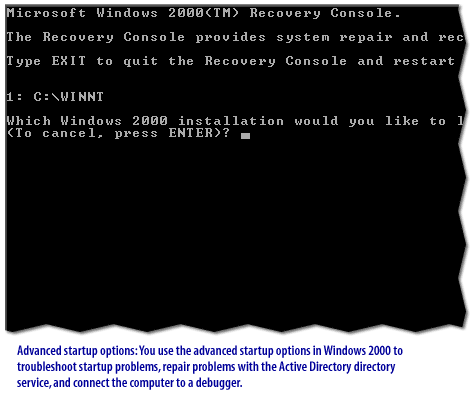
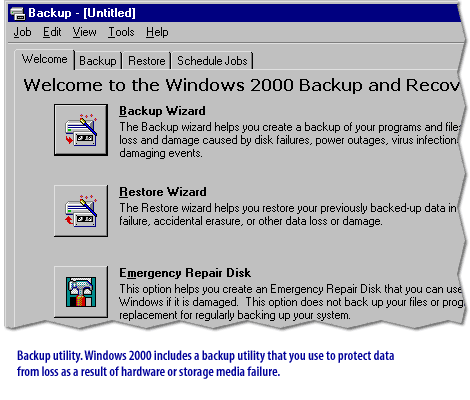
Windows Server 2019 provides the following Protection mechanisms:
Windows Server 2019 provides a variety of disk failure protection mechanisms, including:
Overall, Windows Server 2019 provides a range of disk failure protection mechanisms that can be used to ensure high availability and data protection for mission-critical workloads.
The next lesson looks at implementing fault-tolerant volumes.
- Storage Spaces Direct: This feature allows multiple physical disks to be grouped together into a virtual storage pool, which can then be used to create fault-tolerant volumes using mirroring or parity-based protection. Storage Spaces Direct provides high availability and performance for mission-critical workloads.
- Storage Replica: This feature enables disaster recovery by replicating volumes between different servers or clusters, either synchronously or asynchronously. This allows for rapid failover and recovery in the event of a disaster.
- Resilient File System (ReFS): This file system provides advanced data protection features such as data integrity checks, automatic repair, and data scrubbing. ReFS is designed to detect and correct data corruption in real-time, providing enhanced data reliability and protection against disk failures.
- Dynamic disks: Dynamic disks provide software-based RAID functionality, allowing volumes to be mirrored, striped, or spanned across multiple physical disks. This provides increased performance and fault tolerance for critical data.
Overall, Windows Server 2019 provides a range of disk failure protection mechanisms that can be used to ensure high availability and data protection for mission-critical workloads.
The next lesson looks at implementing fault-tolerant volumes.