| Lesson 4 | Determine disk partition options |
| Objective | Define how and when disk partitioning should be used with Windows. |
Determine Disk Partitioning (Options for Windows )
What are the disk partitioning options for windows?
Question: What are the disk partitioning options for windows?
Windows provides several disk partitioning options, including:
Overall, Windows provides a range of disk partitioning options to meet different needs, from basic partitioning to more advanced fault-tolerant configurations. The choice of partitioning method will depend on factors such as the size of the disk, the type of data being stored, and the need for fault tolerance.
Windows provides several disk partitioning options, including:
- MBR (Master Boot Record): This is the traditional partitioning method used by Windows. MBR supports up to four primary partitions or three primary partitions and one extended partition. The extended partition can contain multiple logical partitions.
- GPT (GUID Partition Table): GPT is a newer partitioning method that supports up to 128 partitions. It is required for booting from a disk larger than 2TB and provides better protection against data corruption.
- Dynamic disks: Dynamic disks allow for more advanced partitioning options, such as creating volumes that span multiple disks or creating fault-tolerant volumes using RAID.
- Simple volume: This creates a single partition that uses all available space on a disk.
- Spanned volume: This combines two or more disks into a single volume that appears as one partition. Data is written sequentially across the disks.
- Striped volume: This combines two or more disks into a single volume that appears as one partition. Data is written in stripes across the disks, which can improve performance.
- Mirrored volume: This creates a fault-tolerant volume by duplicating data on two or more disks.
- RAID-5 volume: This creates a fault-tolerant volume that uses parity information to recover data in case of a disk failure.
Overall, Windows provides a range of disk partitioning options to meet different needs, from basic partitioning to more advanced fault-tolerant configurations. The choice of partitioning method will depend on factors such as the size of the disk, the type of data being stored, and the need for fault tolerance.
What is disk partitioning?
Define how and when disk partitioning should be used with Windows.
Disk partitioning is a way of dividing your physical disk so that each section functions as a separate unit.
When you create partitions on a disk, you divide the disk into one or more areas that can be formatted for use by a file system, such as File Allocated Table (FAT) or the NTFS file system.
Disk partitioning is a way of dividing your physical disk so that each section functions as a separate unit.
When you create partitions on a disk, you divide the disk into one or more areas that can be formatted for use by a file system, such as File Allocated Table (FAT) or the NTFS file system.
How to partition a Disk
Windows provides two built-in methods for partitioning disks:
Create Partition Wizard Overview
- Windows Setup: The Setup program will give you the option of creating a new partition.
Use this method only when creating and sizing the partition on which you will install Windows.
- Windows Disk Management Utility: Once you've installed Windows, use the Disk Management Utility to partition the remaining space on your hard disk. Click the Learning Bridge for a refresher on how to create a partition using the Disk Management Create Partition Wizard.
Partitioning a disk during setup
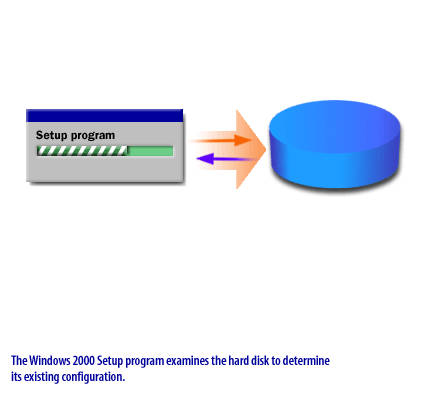
During system setup, you will be presented with different partition options, depending on what the Setup program detects about the system on which you are installing Windows.
In some cases, you will be installing onto a brand new system with no existing partitions, or a system that has had all data removed.
However, in many cases you will be installing onto a system that has already been in use, and you will need to make configuration choices based on those partitions.
Disk partitioning options are only available during setup if you are installing from a CD.
In some cases, you will be installing onto a brand new system with no existing partitions, or a system that has had all data removed.
However, in many cases you will be installing onto a system that has already been in use, and you will need to make configuration choices based on those partitions.
Disk partitioning options are only available during setup if you are installing from a CD.
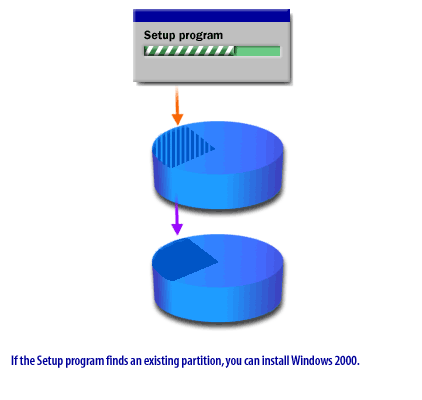
If a partition already exists
If a partition already exists, proceed according to the bullet point below that matches your situation:
- If there's enough unpartitioned disk space to hold Windows, you can install a second partition.
- If the existing partition is large enough to hold Windows, you can install Windows on that partition (without creating a new one). Be aware that if you install an operating system on an existing partition, the new operating system will overwrite the old one.
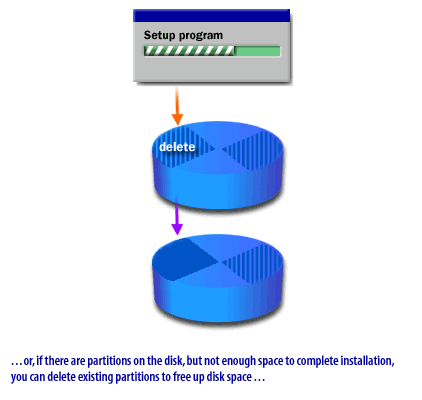
- If there is not enough unpartitioned disk space to hold Windows, nor enough space within the existing partition, you can delete the existing partition, then create a new one.
Deleting existing partition
Deleting an existing partition will render any data on that partition unavailable.
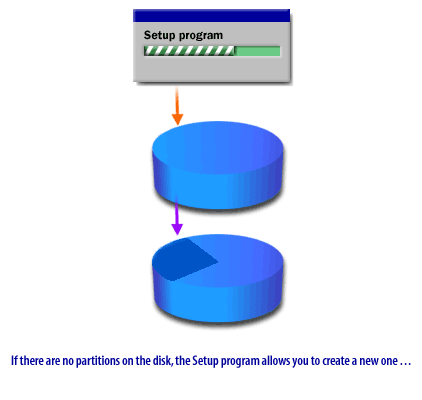
If there is no existing partition
If there is no existing partition, you can create and size a new one for Windows.
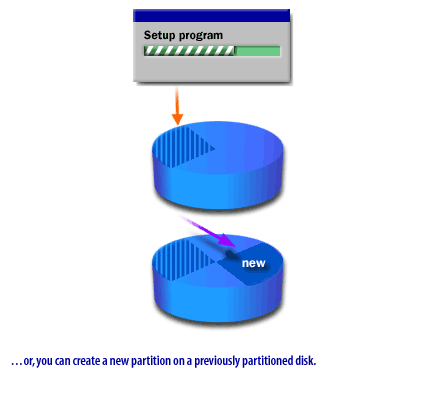
The following series of images illustrates some of the installation partition scenarios you might encounter using Setup to install Windows.
The following series of images illustrates some of the installation partition scenarios you might encounter using Setup to install Windows.
In the next lesson you will learn how to select a file system.