| Lesson 3 | Security standards |
| Objective | Security Standards currently being used |
Security Services and the Standards that Implement Them
A practical map from high-level security services authentication, access control, confidentiality, integrity, and non-repudiation—to the modern standards and mechanisms that make them real.
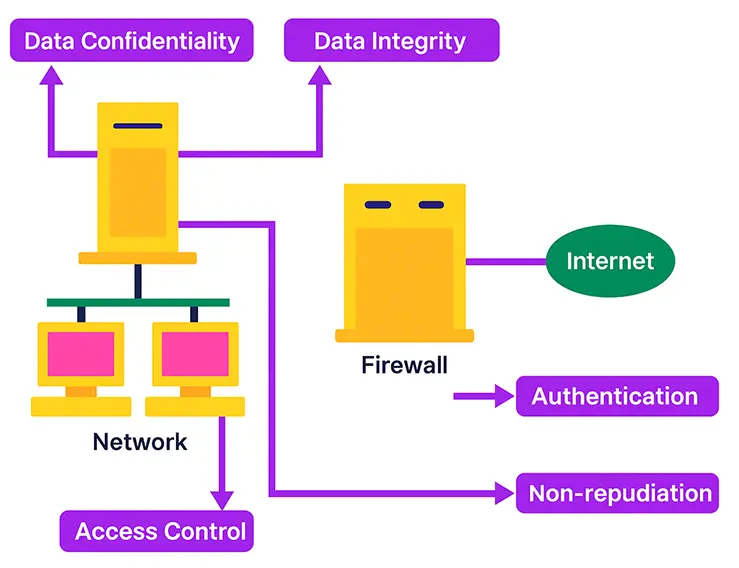
1) Security services (what and why)
Authentication
Proves an entity is who (or what) it claims to be. Typical implementations include passwords with MFA, passkeys/FIDO2, client certificates, or federated identities (OIDC/SAML).
Access Control
Grants or denies actions on resources after authentication—e.g., role-based (RBAC), attribute-based (ABAC), or policy-based (OPA). Apply least privilege and separation of duties.
Data Confidentiality
Prevents unauthorized disclosure. Use strong, modern cryptography (e.g., AES-GCM for data at rest and in transit; TLS 1.2+ with modern ciphers). DES is obsolete; use AES and SHA-256+ for hashing.
Data Integrity
Prevents undetected alteration. Use message authentication codes (e.g., HMAC-SHA-256), digital signatures (Ed25519/ECDSA), checksums, and signed artifacts.
Non-repudiation
Prevents a party from denying an action. Achieved through digital signatures, trusted timestamps, logs with tamper-evidence, and PKI-backed identities.
Network Security and Firewalls
2) Standards (how)
Security frameworks translate the “what” into repeatable “how”. Commonly used standards include:
- ISO/IEC 27001 – ISMS with risk-based controls and continual improvement.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework – Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover.
- PCI DSS – Cardholder data protection for merchants/service providers.
- HIPAA Security Rule – Safeguards for ePHI (US healthcare).
- GDPR – EU personal data protection and accountability.
- SOC 2 – Attestation across Security/Availability/Processing Integrity/Confidentiality/Privacy.
- FISMA / NIST 800-53 – US federal control baselines and assessment rigor.
- CIS Critical Security Controls – Prioritized technical controls to reduce attack surface.
Map each service to controls from these frameworks to get coverage you can audit, measure, and improve.
3) Mechanisms (with examples)
Specific mechanisms
- Confidentiality: AES-GCM, TLS 1.2+; secrets management (KMS/HSM).
- Integrity: HMAC-SHA-256; digital signatures (Ed25519/ECDSA); signed SBOMs/artifacts.
- Authentication: FIDO2/WebAuthn passkeys; OIDC/SAML; client TLS certs.
- Access control: Policy engines (OPA), RBAC/ABAC; Just-in-Time (JIT) access.
- Non-repudiation: PKI + timestamping; immutable audit logs.
Pervasive mechanisms
- Security labels/classification: Data tagging (Public → Restricted).
- Audit and logging: Centralized, immutable, retention+rotation, correlation with SIEM.
- Configuration baselines: CIS Benchmarks; IaC drift detection.
Checksum placement: header vs payload
Header checksums protect routing/metadata; payload checksums (or MACs) protect content. Using both enables precise error handling and integrity guarantees during transport.
4) Governance and compliance tips
- Build a policy matrix mapping each service → standard → control → mechanism → evidence artifact.
- Favor automated evidence (e.g., signed pipeline, policy checks in CI/CD, IaC scans).
- Plan crypto agility: track algorithms/keys; migrate from deprecated ciphers (e.g., DES) to modern suites (AES, SHA-256+).
5) Crawlability note (site ops)
Internal-link health: Our latest crawl recorded
shortestClicksFromHome = 2147483647 for this page—effectively “no discovered path from the homepage.”
Action items: ensure presence in sitemap.xml, add contextual internal links from Module 1/3 index pages,
and verify the page isn’t excluded by robots.txt.
6) Next steps
- Create a service→control→evidence table for this module (exportable CSV for audits).
- Add a cryptography policy sidebar: approved algorithms, key lengths, rotation cadence.
- Instrument integrity and non-repudiation: sign downloadable assets and publish checksums.