| Lesson 2 | Security elements |
| Objective | Most important security elements |
Most Important Security Elements (Modernized)
A resilient security program blends policy, identity, access, cryptography, administration, and audit. This rewrite organizes those elements into a practical, modern workflow aligned to zero-trust principles, current crypto (AES-256, TLS 1.3, SHA-256+), and today’s monitoring and governance practices.
What this lesson covers
- How policy drives identity, access, and encryption decisions.
- How administration and automation enforce controls consistently.
- How audit and telemetry verify effectiveness and guide improvements.
Security Elements Foundation Hierarchy
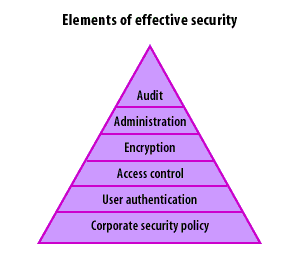
- Corporate security policy: Define objectives, roles, and acceptable use. Use activity logs and metrics (KPIs/KRIs) to measure effectiveness and drive updates.
- User authentication: Enforce phishing-resistant MFA (FIDO2/WebAuthn) and strong lifecycle management for identities (joiner/mover/leaver).
- Access control: Apply least privilege with role-/attribute-based access (RBAC/ABAC), just-in-time elevation, and continuous device posture checks.
- Encryption: Protect data in transit with TLS 1.3 and at rest with AES-256; use modern hashing (SHA-256+) and managed keys (HSM/KMS) with rotation.
- Administration: Codify controls with automation (IaC/PaC), patch SLAs, secure configuration baselines, and ticketed change control.
- Audit: Centralize logs (SIEM/XDR), enable tamper-evident storage, run detections/playbooks (SOAR), and conduct regular reviews and tabletop exercises.
From Policy to Practice: a Logical Workflow
- Author policy and standards: Establish a baseline mapped to NIST CSF/ISO 27001/CIS Controls. Define crypto standards (deprecate DES/MD5), logging minimums, and access requirements.
- Harden identity and endpoints: Centralized IAM, passwordless where possible, EDR on all managed devices, and device health checks before granting access.
- Segment the network: Use zero-trust segmentation, private access for sensitive apps, secure DNS, and minimal inbound exposure.
- Secure the data layer: Classify data; enforce encrypt-at-rest and field-level encryption for sensitive attributes; apply DLP and tokenization where needed.
- Observe and respond: Stream logs to SIEM, correlate with UEBA, and automate responses with SOAR. Track MTTD/MTTR and tune playbooks.
- Audit and improve: Run continuous compliance scans, red/purple-team exercises, and governance reviews; iterate policy and controls based on findings.
Combining Security Methods (Edge and Internal)
Use layered controls across edges and workloads. Examples:
| Security Element | Edge / Gateway Controls | Internal Methods |
| Authorization & Access Control | Next-gen firewall (L7), secure web/app gateways, ZTNA | RBAC/ABAC in apps, OS permissions, JIT/PAM vaulting |
| Identification & Authentication | IdP with FIDO2/WebAuthn, conditional access, device posture checks | Strong password policy where required, SSO/OIDC/SAML, session management |
| Encryption & Integrity | TLS 1.3 termination, HSTS, DNS over TLS/HTTPS | AES-256 at rest, SHA-256+ hashes, KMS/HSM, key rotation & envelope encryption |
| Monitoring & Audit | Network telemetry, IDS/IPS, egress controls | SIEM/XDR, UEBA, immutable log storage, compliance reporting |
Quick Start: Policy Skeleton (copy/paste)
Title: Enterprise Security Baseline (v1.0)
Scope: Corp | Cloud | Third Parties
Identity
- Enforce MFA (FIDO2/WebAuthn); SSO for all apps
- Quarterly access reviews; JIT for privileged roles
Crypto
- TLS 1.3 only; deprecate legacy ciphers
- AES-256 at rest; SHA-256+; keys in KMS/HSM; rotate ≤ 180 days
Monitoring
- Centralize logs (SIEM); UEBA enabled
- Incident playbooks in SOAR; test quarterly
Change
- IaC/PaC with 4-eyes review; SBOM required in builds
- Patch SLAs: Critical ≤ 7 days; High ≤ 15 days
Notes on legacy terms (updated)
- Screening router → treat as packet filter or firewall policy tier.
- Firewall token → prefer modern IdP-issued tokens (OIDC JWTs) with short lifetimes and audience binding.
- Remote access devices → use VPN with MFA or ZTNA for per-app access.