| Lesson 7 | Providing a DHCP service for a routed network |
| Objective | Describe how a DHCP Server services non-Microsoft hosts. |
Providing DHCP Service for Routed Network
When DHCP clients receive IP address assignments, they retain the address for a defined lease duration, which can be renewed periodically. In contrast, BOOTP clients, often used in diskless systems or embedded devices, do not support leasing; instead, they are typically assigned static IP configurations from the DHCP server.
Windows Server 2022 DHCP is designed to interoperate with virtually any standards-compliant DHCP client. Whether you're running Linux, macOS, NetWare, or UNIX-based systems, as long as the client adheres to the DHCP specifications, the Windows DHCP server will respond to its requests. However, it is important to note that not all third-party operating systems may support every DHCP option defined on the Windows Server. Despite this, such systems can still obtain essential network parameters, including:
- IP address
- Subnet mask
- Default gateway
- DNS server (if supported)
Note: The DHCP service in Windows Server 2022 supports all clients that comply with RFC 951, RFC 2131, and RFC 2132—the foundational specifications for BOOTP and DHCP. For further details, refer to the appropriate RFC documentation.
📘 Client Support – Windows Server 2022 DHCP Service
The DHCP service in Windows Server 2022 is designed to support a wide range of client types across modern enterprise networks, including both Microsoft and non-Microsoft systems. Below is an overview of supported client types and guidance for managing them.
-
✅ Non-Microsoft DHCP Clients
Windows Server 2022 DHCP supports standards-compliant DHCP clients running on operating systems such as:
- Linux
- macOS
- BSD variants
- IoT devices
- Network appliances
- VMs or containers on platforms like VMware, Hyper-V, or Docker
These clients typically adhere to the DHCP protocol as defined in RFC 2131 and RFC 2132. While core options such as IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers are universally supported, some clients may not recognize Microsoft-specific or vendor-defined options.
📌 Recommendation: When deploying non-Windows clients, test compatibility with required DHCP options in your environment, especially for advanced configurations such as PXE boot or option 43 (vendor-specific options).
-
⚠️ BOOTP Clients (Legacy Support)
Support for BOOTP (Bootstrap Protocol) is still included in Windows Server 2022 for legacy systems, but use is discouraged in modern environments due to the protocol's limitations (e.g., lack of leasing and limited configuration options).
- BOOTP clients typically request an address at startup and do not maintain a lease.
- Windows Server 2022 can issue dynamic addresses to BOOTP clients from a designated BOOTP address pool.
- The server can be configured to reclaim BOOTP-assigned IP addresses after verifying that they are no longer in use (e.g., via address conflict detection or ping checks).
⚠️ Note: BOOTP should be phased out in favor of full DHCP support whenever possible.
-
🛠️ Statically Configured (Non-DHCP) Clients
Some network infrastructure devices (e.g., firewalls, printers, domain controllers, hypervisors) may require manually configured static IP addresses outside the DHCP scope.
- These devices do not request leases from the DHCP server.
- You can document their IP usage by creating exclusions in the DHCP scope to prevent conflicts.
- Reservations in DHCP should only be used for DHCP-enabled clients tied to specific MAC addresses.
Best Practice: Maintain a centralized inventory of static IP addresses and ensure they do not overlap with dynamic scopes.
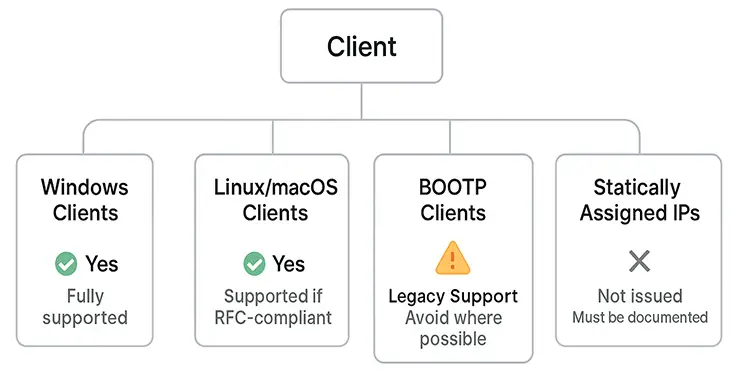
| Client Type | DHCP Support | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Clients | ✅ Yes | Fully supported |
| Linux/macOS Clients | ✅ Yes | Supported if RFC-compliant |
| BOOTP Clients | ⚠️ Legacy | Supported but deprecated; avoid where possible |
| Statically Assigned IPs | ❌ Not issued | Must be documented and excluded from dynamic scope |
The next lesson wraps up this module.