| Lesson 5 | User auditing |
| Objective | Describe user auditing in Redhat Linux. |
Examining System Logs in Red Hat Linux
User auditing refers to examining the system logs to determine information about user access. It is similar to process auditing in that it provides detailed information; however, this information is based on users instead of processes. You should maintain long-term statistics, by summarizing and combining statistics after you rotate the logs. User auditing examines user access and provides you information on what users have done, where they have connected from, when they have connected, and how long they stayed connected. Support is provided for examining the resource usage of a particular user, based on the process accounting logs. The
The SlideShow below shows you examples of these commands and the output they generate.
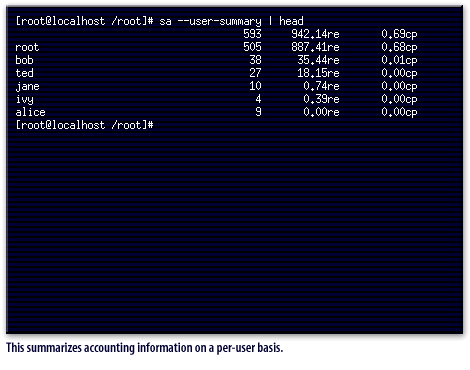
sa command provides you summarized accounting information on a per-user basis.
The dump-utmp command provides a raw dump of the utmp file; however, it is of little use unless you are very familiar with the file format. There are also commands that will aid you in determining when and how long users stay online. You can use the --user-summary argument to identify how long users remain online.
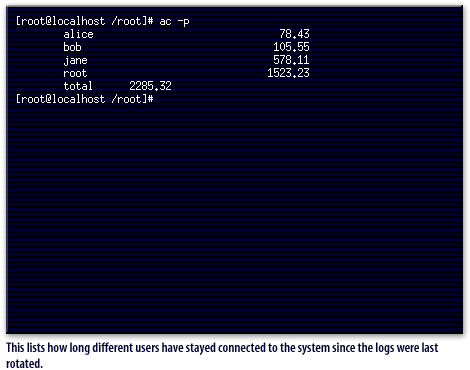
Also, the ac command lists how long different users have stayed connected to the system since the logs were last rotated.
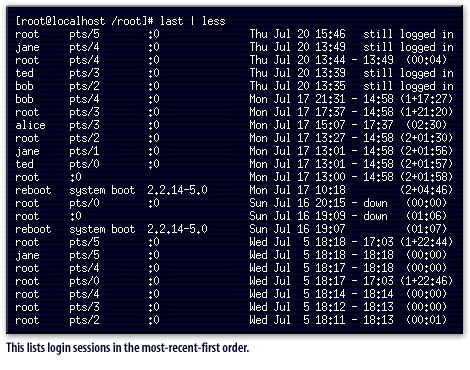
The lastcomm command provides listings of when users connected, where they connected from, and for how long. This command lists login sessions, optionally of a specified user, in most-recent-first order. The SlideShow below shows you examples of these commands and the output they generate.
Best Approach for examining System Logs
The best approach for examining system logs in Red Hat Linux is to use the "journalctl" command.
"journalctl" is a command-line utility for querying and displaying system logs collected by the systemd journal. It provides a comprehensive view of system activity, including kernel messages, system services, and application logs.
Using "journalctl", you can filter the logs based on various criteria, such as time range, log level, and specific services or units. You can also view the logs in various formats, including plain text, JSON, and XML.
Here are some useful "journalctl" commands for examining system logs in Red Hat Linux:
By using "journalctl" to examine system logs in Red Hat Linux, you can gain valuable insights into system activity and diagnose any issues that may arise.
"journalctl" is a command-line utility for querying and displaying system logs collected by the systemd journal. It provides a comprehensive view of system activity, including kernel messages, system services, and application logs.
Using "journalctl", you can filter the logs based on various criteria, such as time range, log level, and specific services or units. You can also view the logs in various formats, including plain text, JSON, and XML.
Here are some useful "journalctl" commands for examining system logs in Red Hat Linux:
- View all logs: "journalctl"
- View logs for a specific service: "journalctl -u <service-name>"
- View logs for a specific time range: "journalctl --since=<start-time> --until=<end-time>"
- View logs with a specific log level: "journalctl -p <log-level > "
- View logs in reverse chronological order: "journalctl -r"
- View logs in a specific format: "journalctl -o <output-format>"
Red Hat User Auditing
The next lesson explains how to use logfiles for accounting and auditing.
The next lesson explains how to use logfiles for accounting and auditing.
Click the link below to read more about process user auditing.
Process User Auditing
Process User Auditing