| Lesson 9 | Optimize performance and security for remote administration |
| Objective | Adjust the performance and security settings for remote administration. |
Optimizing Performance for Remote Administration and Security on Windows Server 2022
For Windows Server 2022, Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is often a target for performance tuning and hardening against attacks.
Let us break it down clearly into two sections: Performance and Security.
🛠️ 1) Adjusting *Performance* Settings for Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2022
Summary
🛠️ 1) Adjusting *Performance* Settings for Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2022
| Setting/Area | Action | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Session Limits | Configure session timeouts and idle session limits (via Group Policy: Computer Configuration > Admin Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Session Time Limits). |
Prevent abandoned sessions from consuming server resources. |
| RemoteFX Compression Settings | Tune compression settings for better bandwidth utilization (policy: Computer Configuration > Admin Templates > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Remote Session Environment > Configure compression for RemoteFX). |
Lower compression can improve responsiveness at the cost of slightly higher bandwidth. |
| Fair Share Scheduling | Enable CPU and Disk Fair Share (Computer Configuration > Admin Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections). |
Balances CPU/disk I/O among sessions to prevent resource hogging. |
| TCP Tuning | Adjust TCP parameters (e.g., TCP Chimney Offload, Receive Side Scaling (RSS), NetDMA) using netsh int tcp set global commands. |
Enhances network throughput for RDP sessions. |
| Graphics Performance | Set "Optimize for performance" under RemoteFX graphics policies; limit unnecessary visual effects. | Reduces unnecessary GPU load for simple desktop tasks. |
| RDP Connection Quality Settings | Disable or tune features like font smoothing, desktop background, animation, and menu/window fading through RDP settings. | Saves bandwidth and CPU usage during sessions. |
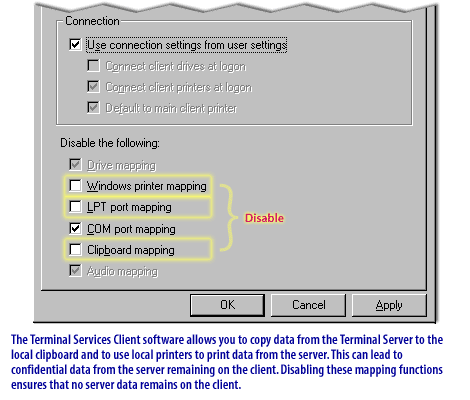
| Printer and Drive Redirection | Disable unneeded redirection settings unless necessary (Computer Configuration > Admin Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Device and Resource Redirection). |
Avoids resource use from unnecessary device mappings. |
| Setting/Area | Action | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Network Level Authentication (NLA) | Require NLA for all connections (Computer Configuration > Admin Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Security > Require user authentication for remote connections). |
Protects against unauthorized access before session creation. |
| Strong Passwords and MFA | Enforce strong password policies and implement MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication). | Drastically reduces the chance of brute-force or credential stuffing attacks. |
| Restrict RDP Access | Use firewalls, VPNs, or Network Security Groups (NSGs) to restrict RDP access to trusted IP addresses only. | Limits attack surface area. Never expose RDP directly to the public internet. |
| Account Lockout Policies | Set lockout thresholds (Account Policies > Account Lockout Policy). Example: 5 failed attempts, 15 min lockout. |
Prevents brute force attacks on RDP login. |
| Audit and Logging | Enable detailed RDP session logging and failed login audit logs (Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > Logon/Logoff). |
Helps you detect unusual or suspicious activity. |
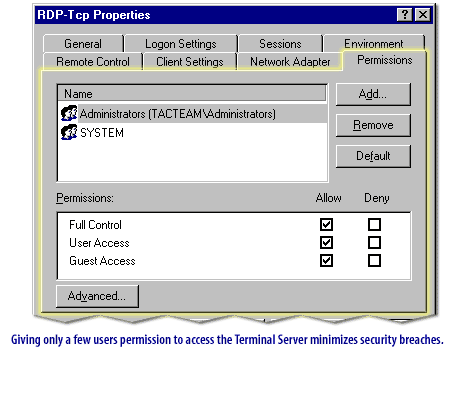
| Limit Admin Rights | Only allow specific users/groups remote desktop access through the “Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services” setting. | Principle of least privilege minimizes damage if credentials are stolen. |
| TLS Encryption for RDP | Force RDP encryption to use TLS 1.2 or higher (Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration or Group Policy). |
Encrypts session data fully and disables older, weaker encryption. |
| Disable Clipboard and Drive Redirection | Disable if unnecessary (Computer Configuration > Admin Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Device and Resource Redirection). |
Prevents exfiltration or infection through redirected devices. |
| Group Policy: RDP Session Security Layer | Set the "Security Layer" setting to SSL (TLS 1.2) only (Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Security). |
Ensures the RDP session cannot fall back to less secure protocols like RDP Security Layer. |
| Session Timeout and Disconnection Policies | Force automatic disconnection/logoff for idle or disconnected sessions. | Reduces risk from abandoned open sessions. |
| RDP Gateway (Optional) | Deploy RDP Gateway server if users need to access internal RDS hosts externally. | Adds an extra authentication and inspection layer. |
| Use Certificates for RDP | Install a valid SSL certificate for RDP host instead of self-signed certs. | Improves trust and prevents man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. |
Summary
| Focus Area | Key Steps |
| Performance | Tune session limits, enable Fair Share, optimize graphics/compression, disable unneeded redirection. |
| Security | Enforce NLA, use TLS encryption, limit users/IPs, enable audit logs, force strong authentication, consider RDP Gateway. |
📌One-Liner Checklist to Start With
# For performance Enable Fair Share Scheduling Disable Unneeded Device Redirection Optimize RDP graphics settings # For security Enforce NLA Restrict RDP to specific IPs/firewalls Use strong passwords and MFA Force TLS 1.2 encryption Audit login attempts Set idle session timeouts
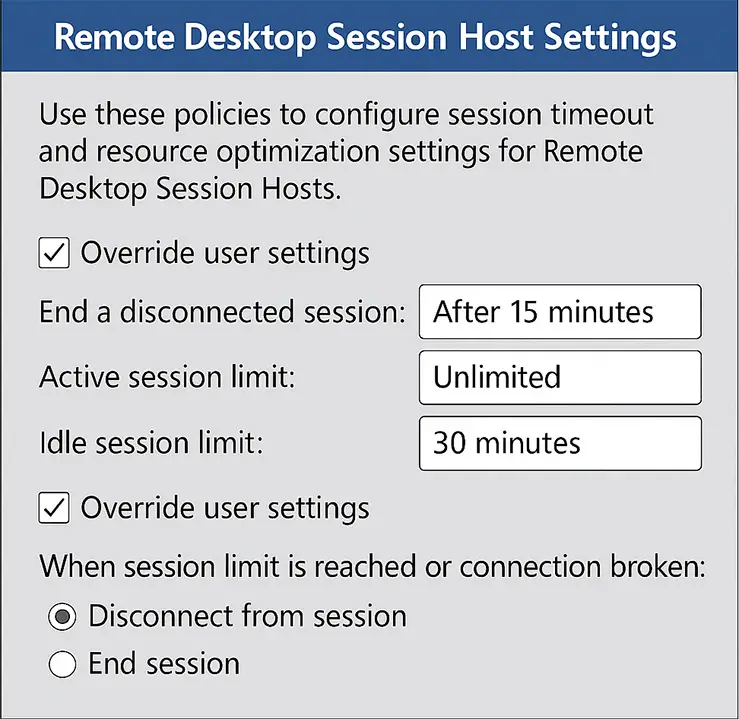
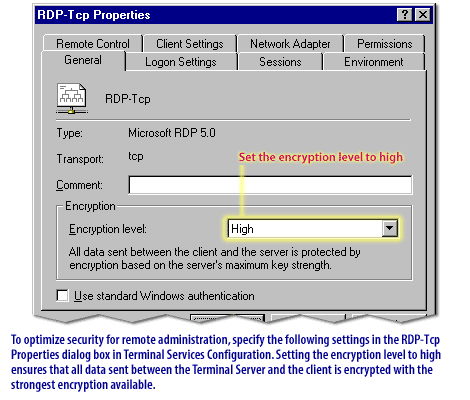
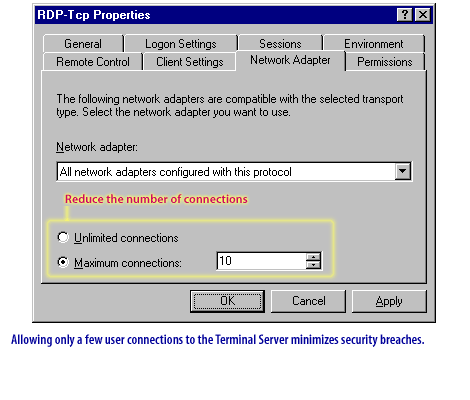
Configuring Remote Desktop Services for remote administration requires settings that differ from those used in multi-session deployment environments. To optimize performance and security for administrative access, configure the appropriate policies in Remote Desktop Session Host settings and Group Policy Management.
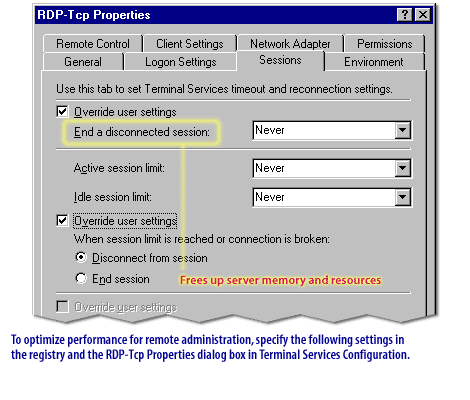
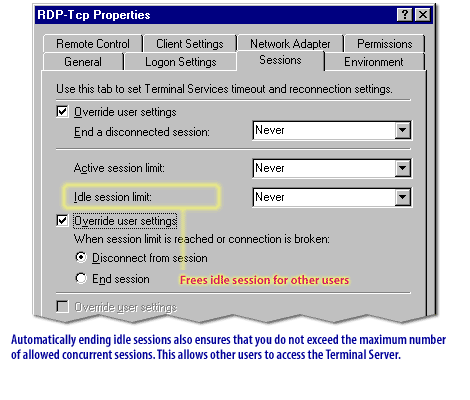
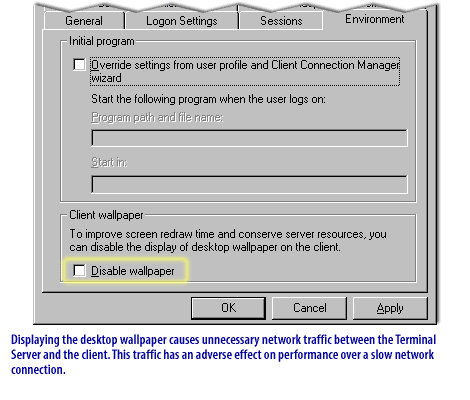
The next lesson concludes this module.
Optimize Performance Security - Exercise
Click the Exercise link below to check your knowledge of installation and configuration of Terminal Services.
Optimize Performance Security-Exercise
Optimize Performance Security-Exercise